“Wine Will Clean Your Brain!”
There was a recent study and it’s been of interest to wine drinkers everywhere.
The study explored the long-term effects of alcohol on the central nervous system (e.g. your brain). Some of the reporting out there has come with some pretty snappy headlines (e.g. “Wine will clean your brain!”) Naturally, you’re probably a bit skeptical. So let’s take together a closer look.
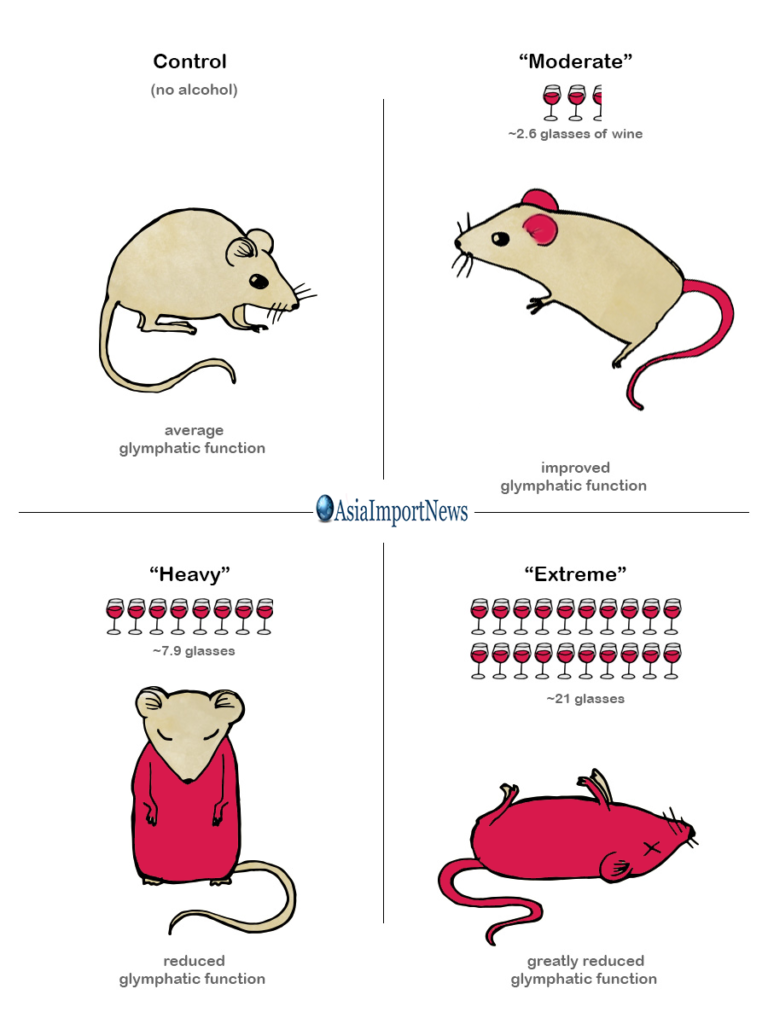
The study studied alcohol’s effect on the brain’s waste removal system (the glymphatic system). Look at the result.
The Alcohol Brain Study
The Center for Translational Neuromedicine at The University of Rochester published on February 2018 a study about the effects of prolonged alcohol exposure on the central nervous system. In their study, they exposed mice to various levels of ethanol (alcohol) in small, intermediate, and high doses. They were trying to pinpoint how much alcohol it takes to damage central nervous system function. For their metric, they observed the glymphatic system. The results were unexpected.
What Is The Glymphatic System? Think of it as the waste removal system of your brain. It’s the distribution network of crucial compounds (glucose, amino acids, neurotransmitters) through your central nervous system.
What Did The Study Find?
Good News
Low: (0.5 g/kg per day) = Equivalent to 2.63 Glasses of Wine a Day (Moderate Drinking)
Findings showed that the glymphatic function in mice improved with a low-dose exposure to ethanol. In human terms, it would be equivalent to about 2 and a half glasses of wine (for a 155 lb / 70 kg human). The exposure to ethanol also reduced inflammation and increased efficiency of waste removal in the brain.
Bad News
Medium: (1.5 g/kg per day) = Equivalent to 7.9 Glasses of Wine a Day (Binge Drinking)
High: (4 g/kg per day) = Equivalent to 21 Glasses of Wine a Day (Sheer Insanity)
Unfortunately, the intermediate- (1.5 g/kg) and high-dose (4 g/kg) exposures majorly decreased the glymphatic function of the mice, resulting in suppressed activity, misallocation of compounds, and induced an injury reaction in the cells. The authors suggested that these adverse reactions likely increase the risk of dementia.
Drink Smarter – Wine may taste magical, but it isn’t magic.
Sources: